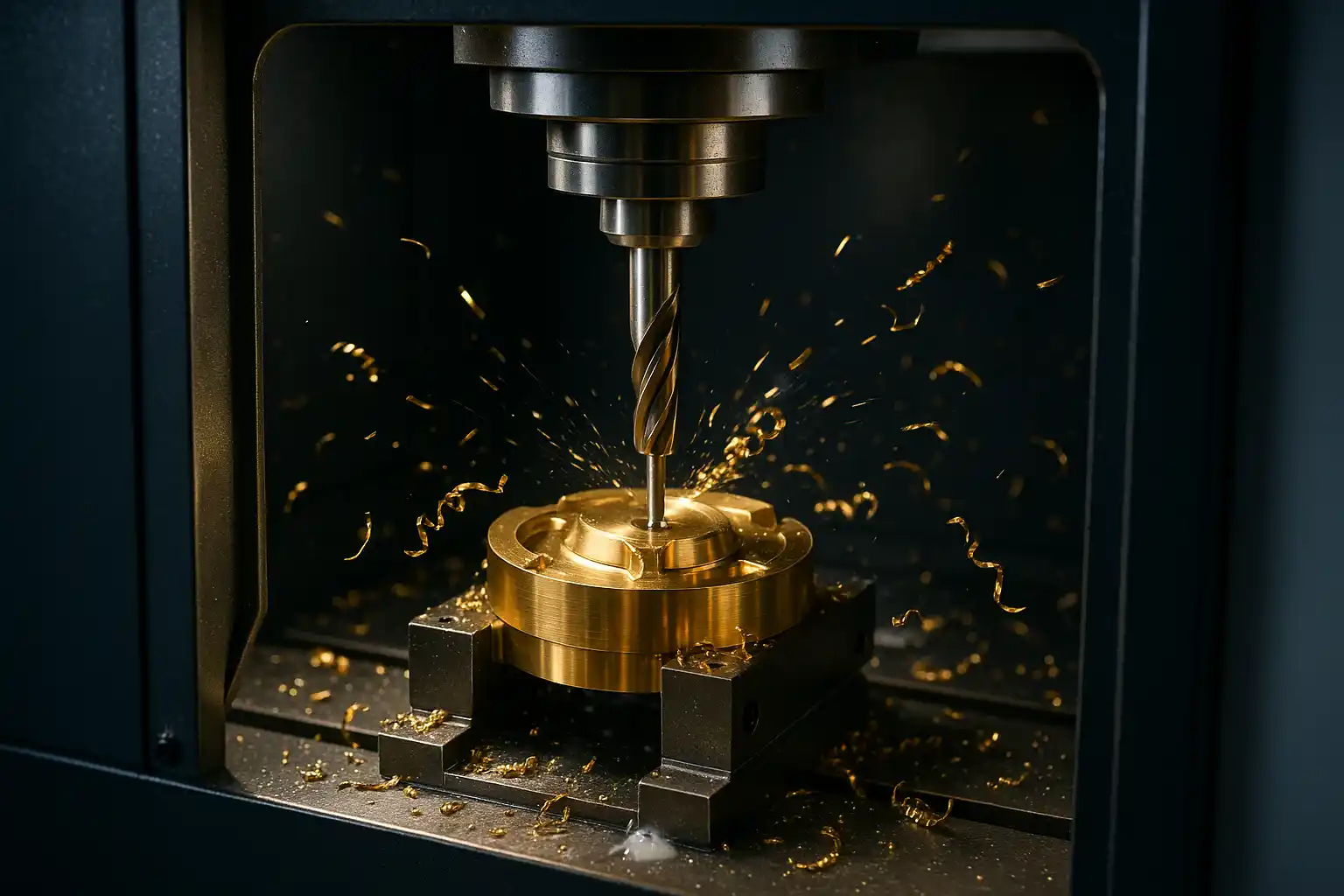
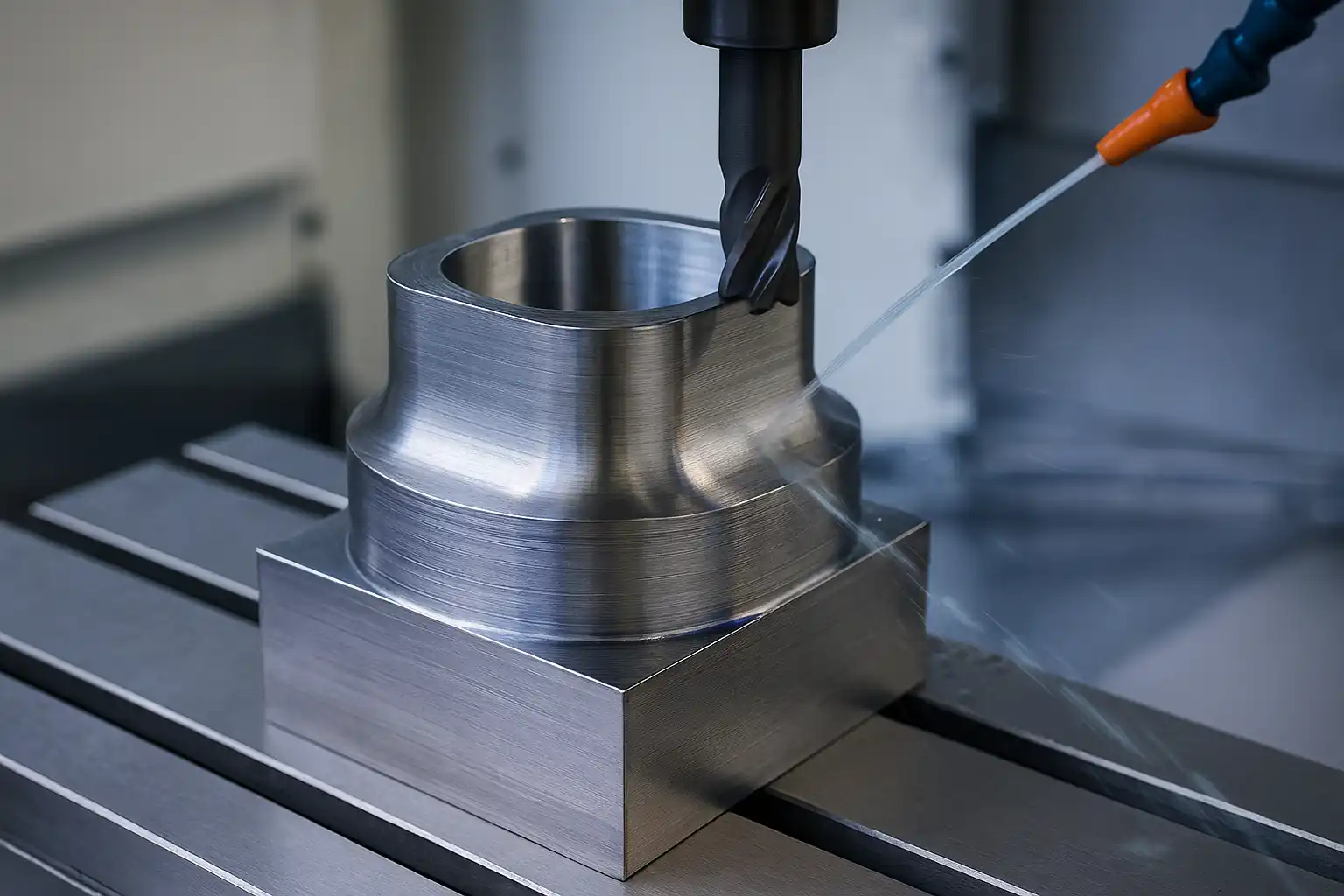
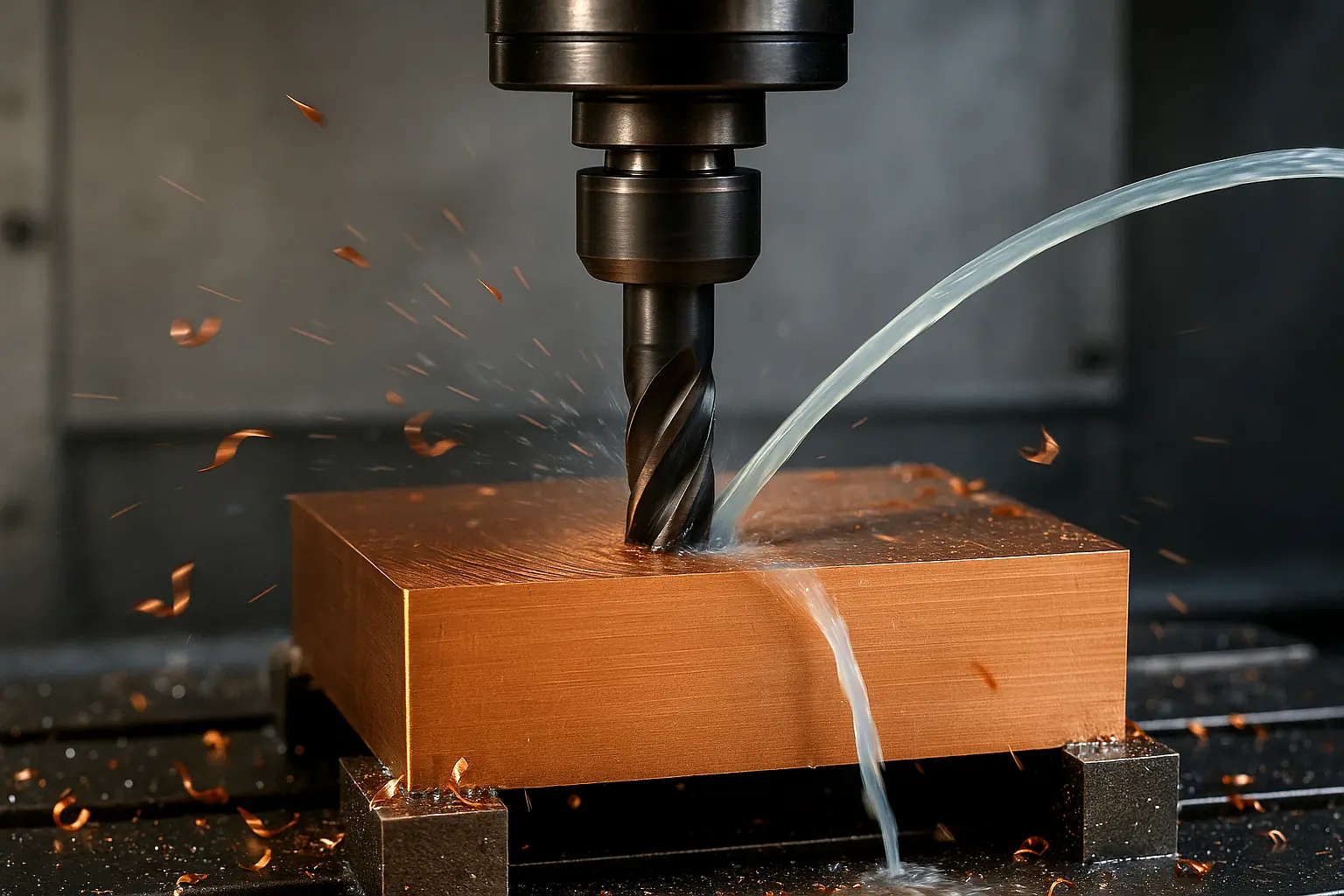
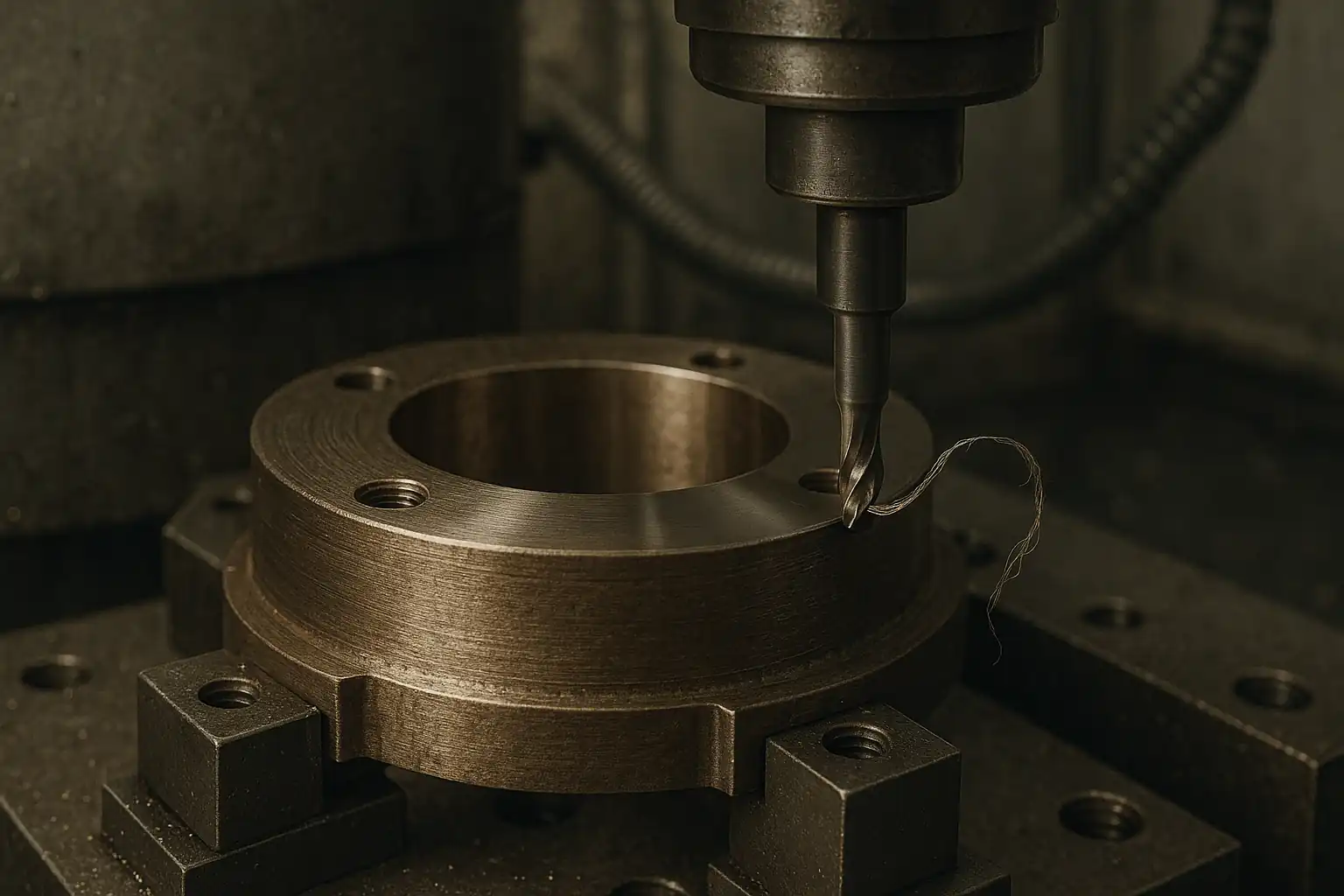
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, and the precise ratio of these two metals gives it unique physical properties and excellent machinability. This guide aims to fully reveal how this ancient material has been reborn with the help of modern CNC machine tools. We will take you on a journey to explore the complete lifecycle of CNC brass machining, from the manufacturing process of the material itself and its core properties, to the definition of the process, and its common grades.
What is Brass Machining?
Brass machining is the manufacturing process of precisely shaping brass raw materials into finished parts using computer numerical control (CNC) machines. As an efficient subtractive manufacturing technique, CNC brass machining uses automated programming to control milling, turning, and drilling operations, quickly and accurately cutting the brass to produce a wide range of high-precision, complex components.
Thanks to brass’s exceptional machinability and superior material properties, brass machining is widely used to create critical parts for various industries.
Brass Manufacturing Process
Before we dive into CNC machining, understanding how brass material itself is made helps us better appreciate its properties. The brass manufacturing process primarily involves melting, casting, and subsequent plastic working, which together determine the final material’s physical properties and machinability.
Melting and Casting
This is the first step in creating brass. Pure copper and pure zinc, along with other necessary alloying elements like lead or tin, are precisely mixed and melted in an electric or induction furnace to form a homogenous brass alloy liquid.
The molten liquid is then poured into molds for casting. Continuous casting is a common method used to produce the rods and profiles used for CNC machining, as it ensures a dense and uniform material structure. For parts with complex shapes, such as valve bodies, sand casting is typically used.
Hot and Cold Working
After casting, the brass ingots or rods undergo further plastic deformation to refine their microstructure and mechanical properties.
- Hot Working: The material is extruded or rolled at high temperatures. This process effectively eliminates casting defects, refines grain size, and improves the material’s density and uniformity, making it more suitable for subsequent machining.
- Cold Working: The material is drawn or cold-rolled at room temperature. Cold working significantly increases brass’s strength and hardness but reduces its ductility. Grades requiring high ductility, like C26000, are often cold-worked and then annealed to achieve the desired properties.
Ultimately, through these complex manufacturing processes, brass is delivered to customers in the form of rods, plates, or tubes that are ready for CNC machining.
Why Choose Brass for CNC Machining?
Brass is a top choice for CNC machining not just because it’s easy to work with, but because of its exceptional blend of physical and chemical properties. These characteristics give machined brass parts immense value across a wide range of applications.
- Excellent Machinability: This is brass’s most famous quality. The alloy’s composition, primarily copper and zinc, allows it to produce short, brittle chips during cutting. This reduces tool wear, extends tool life, and enables faster machining speeds, leading to higher production efficiency. For large-scale manufacturing and complex parts, this property is crucial.
- Superior Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Brass is a great conductor of both electricity and heat. This makes it an essential material in the electronics industry for components like connectors, terminals, heat sinks, and switches, ensuring the efficient transfer of current and heat.
- Good Corrosion Resistance: Brass offers excellent resistance to corrosion from atmospheric conditions, water, and certain chemicals. Specialized grades, like lead-free brass, have enhanced corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in drinking water systems, valves, and marine environments.
- Unique Mechanical Properties: Brass provides a great balance of strength, hardness, and ductility. By adjusting the ratio of copper to zinc, manufacturers can produce different brass grades with specific properties to meet various application demands. For example, brass with a higher zinc content is typically harder, while a higher copper content results in better ductility and toughness.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The signature golden color of brass gives parts a high-quality visual finish. This natural beauty makes it a popular choice for decorative items, musical instruments, architectural hardware, and art pieces, where aesthetics are just as important as function.
- High Recyclability: Brass is an eco-friendly material that is 100% recyclable. This not only lowers production costs but also aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Common Machinable Brass Grades

While there are many brass grades, not all are suitable for machining. The table below lists the most common and popular brass grades used in CNC machining, along with their properties and typical applications.
| Grade (UNS) | Common Name | Key Machinability Traits | Typical Applications |
| C36000 | Free-Cutting Brass | Excellent. Unmatched cutting performance, the gold standard for high-speed automated machining. | Screws, nuts, valve parts, gears, bearings, connectors |
| C26000 | Cartridge Brass | Good. Highly ductile, but chip management is needed to avoid stringy chips. | Cartridge cases, automotive radiators, bellows, rivets |
| C46400 | Naval Brass | Good. Balances machinability with superior corrosion resistance. | Marine hardware, pump shafts, bolts, valve stems |
| C69300 | Eco-friendly Lead-Free Brass | Good. Lead-free and environmentally compliant, with machinability similar to C36000. | Drinking water pipe fittings, faucets, valves |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are the answers to some of the most common questions we get about CNC brass machining.
Q: Why is brass easy to machine?
A: The key to brass’s excellent machinability lies in its alloy composition. The presence of zinc (or lead) helps create short, manageable chips during cutting. This reduces tool wear, simplifies chip evacuation, and allows for higher cutting speeds, which significantly boosts production efficiency.
Q: What is the best brass for machining?
A: From a machinability standpoint, C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass) is generally considered the best choice. It’s specifically engineered for high-efficiency machining, producing very short chips that allow for higher cutting speeds and a longer tool life, making it ideal for large-scale, automated production.
Q: How difficult is brass to machine?
A: Brass is relatively easy to machine. Compared to materials like stainless steel or titanium, brass is softer and requires less cutting force. Its inherent machinability means it is often easier to manage chips than aluminum and causes less tool wear.
Q: Is brass machining expensive?
A: While the raw material cost of brass is typically higher than aluminum or some steels, the overall cost of CNC brass machining can be lower. Higher production efficiency, longer tool life, and fewer post-processing requirements make brass a highly cost-effective choice for high-volume production.
Conclusion
In summary, brass holds an indispensable place in modern CNC machining due to its excellent machinability, good electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It is not just a metal; it is a perfect combination of efficiency, precision, and durability.
Whether you’re looking for highly conductive connectors for the electronics industry, corrosion-resistant valves for plumbing systems, or high-quality decorative parts for architectural design, brass provides a reliable solution. By understanding the properties and machining advantages of brass, you can confidently choose this material and bring exceptional value to your projects. If you’re ready to start your next brass machining project, contact our team today to get a custom quote and expert consultation.