What Does SFM Mean in Machining? How to Calculate and Use It
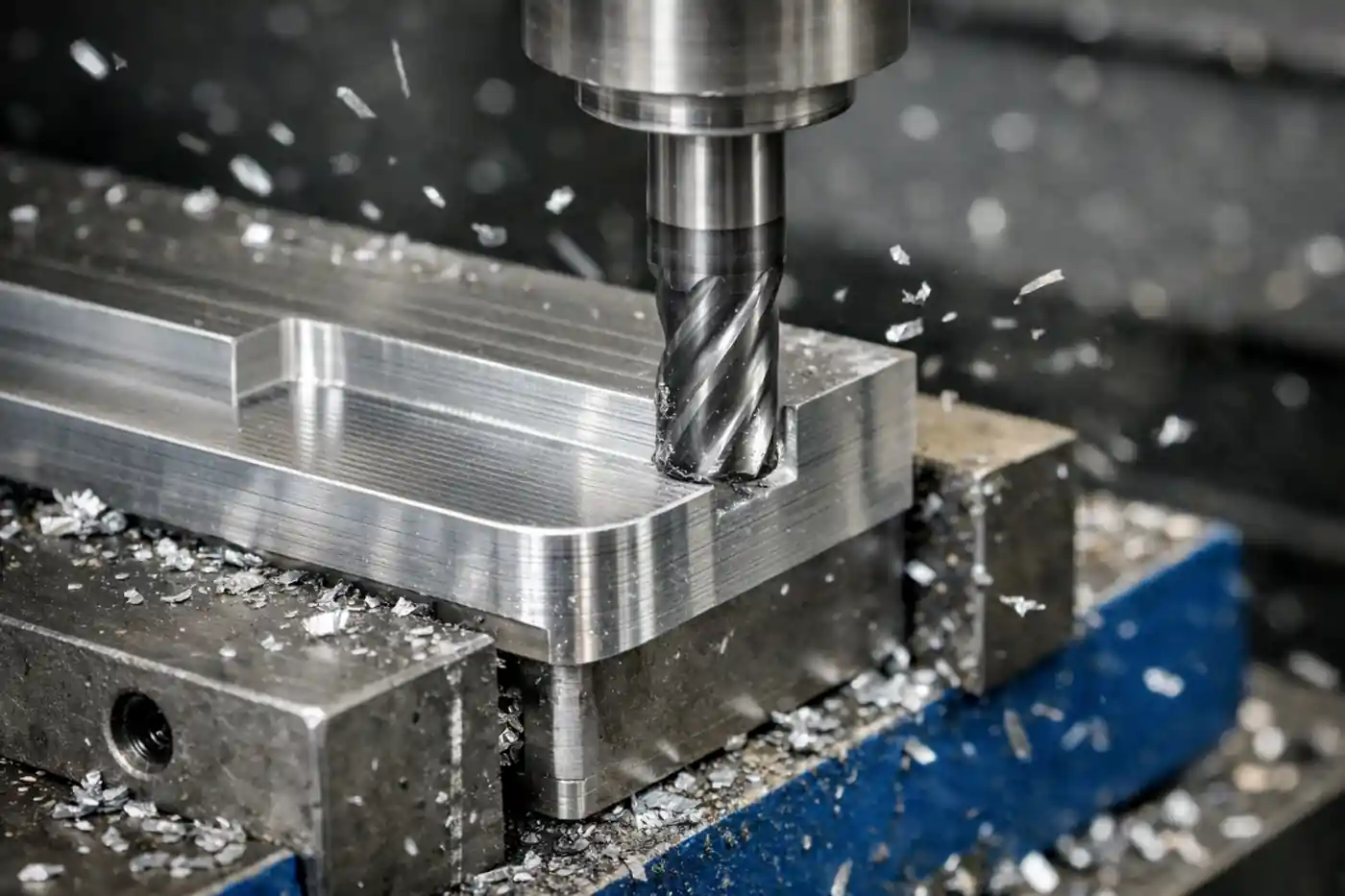
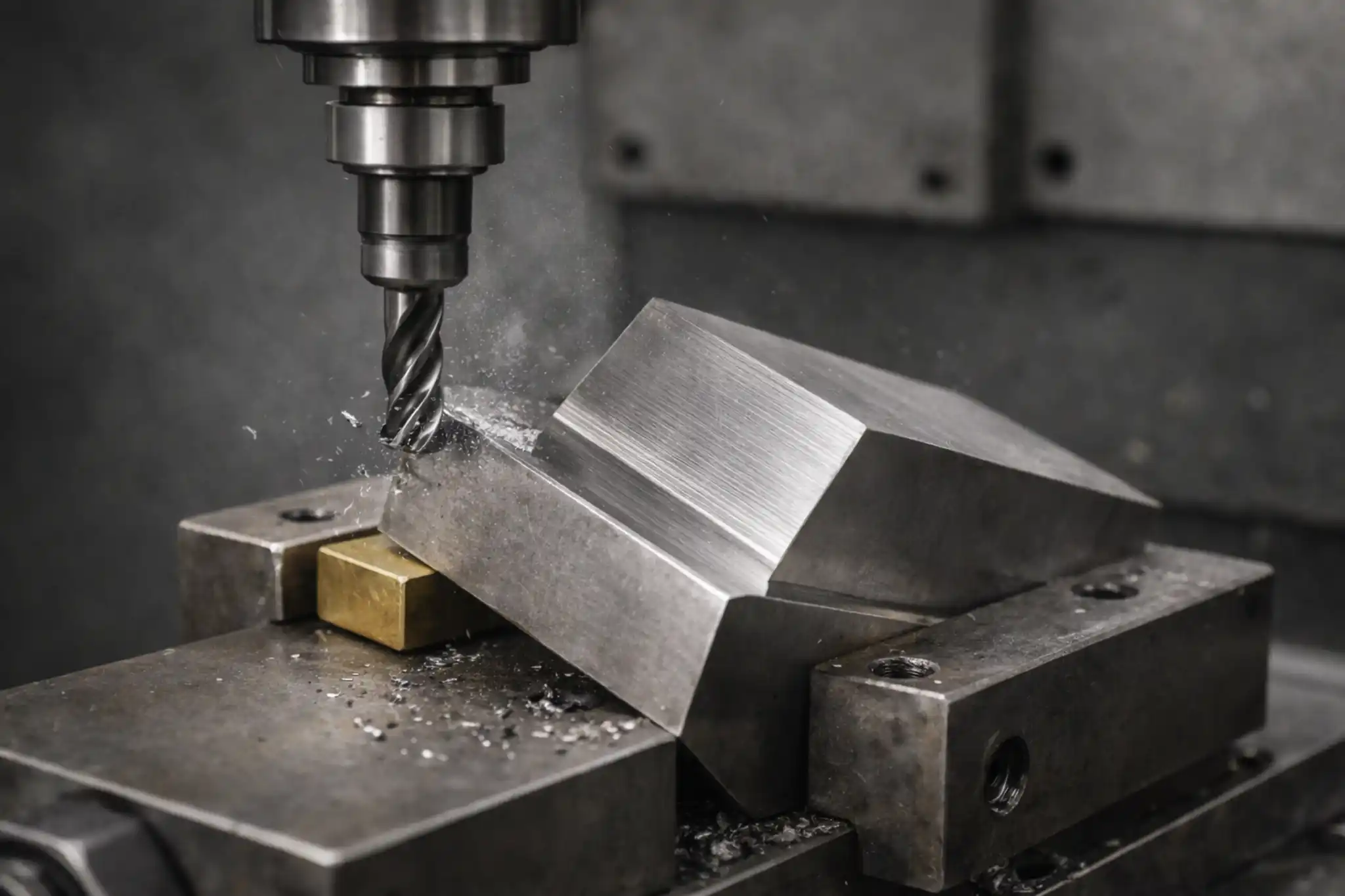
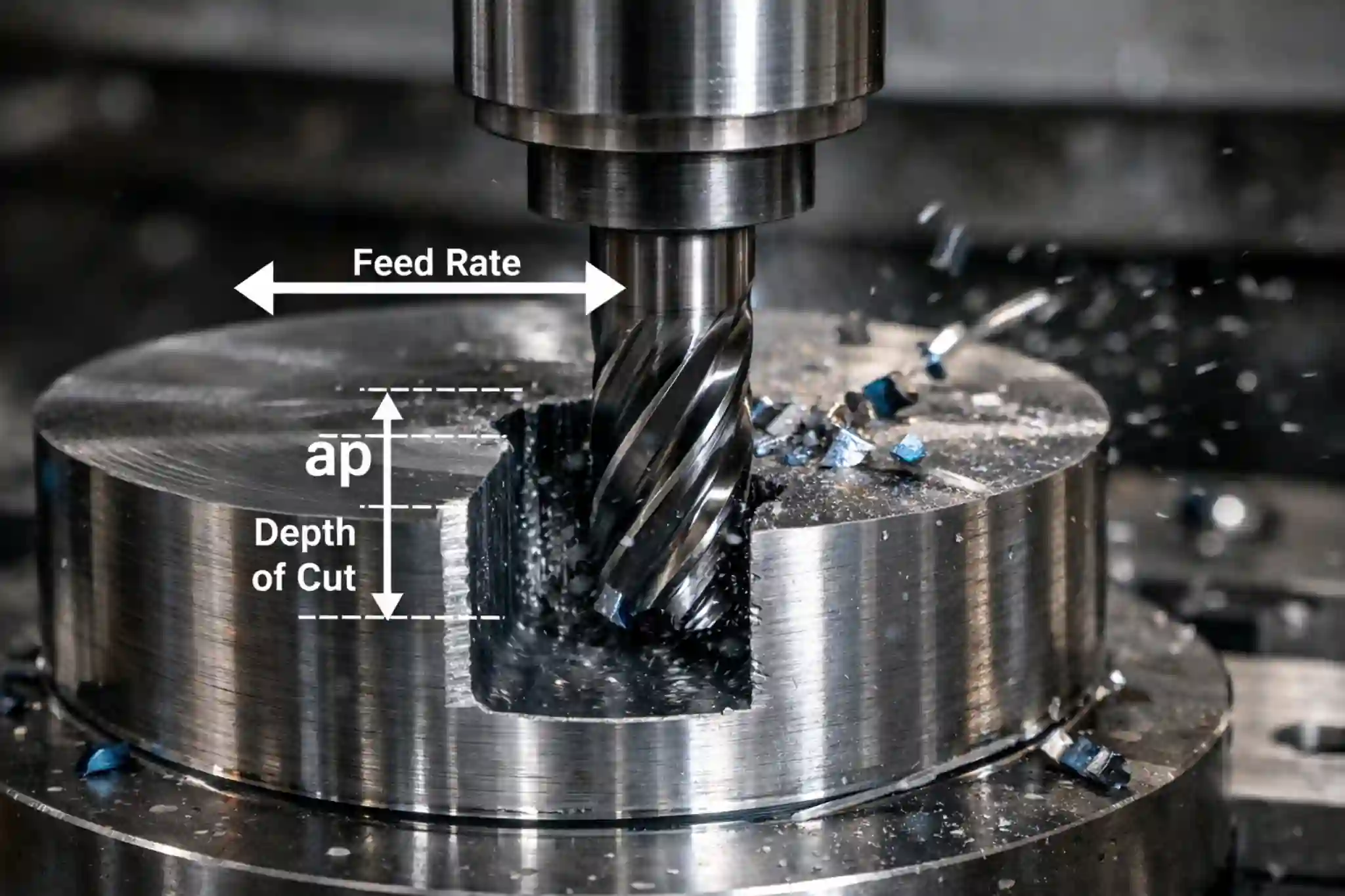
SFM (Surface Feet per Minute) is a core parameter used to measure cutting speed and an important reference when setting machining conditions. It affects not only cutting heat and tool life, but also surface finish, chip evacuation, and overall machining efficiency. This article explains the basic concept of SFM, how it is calculated, how it differs from RPM, and the recommended ranges and common setting mistakes for different materials.