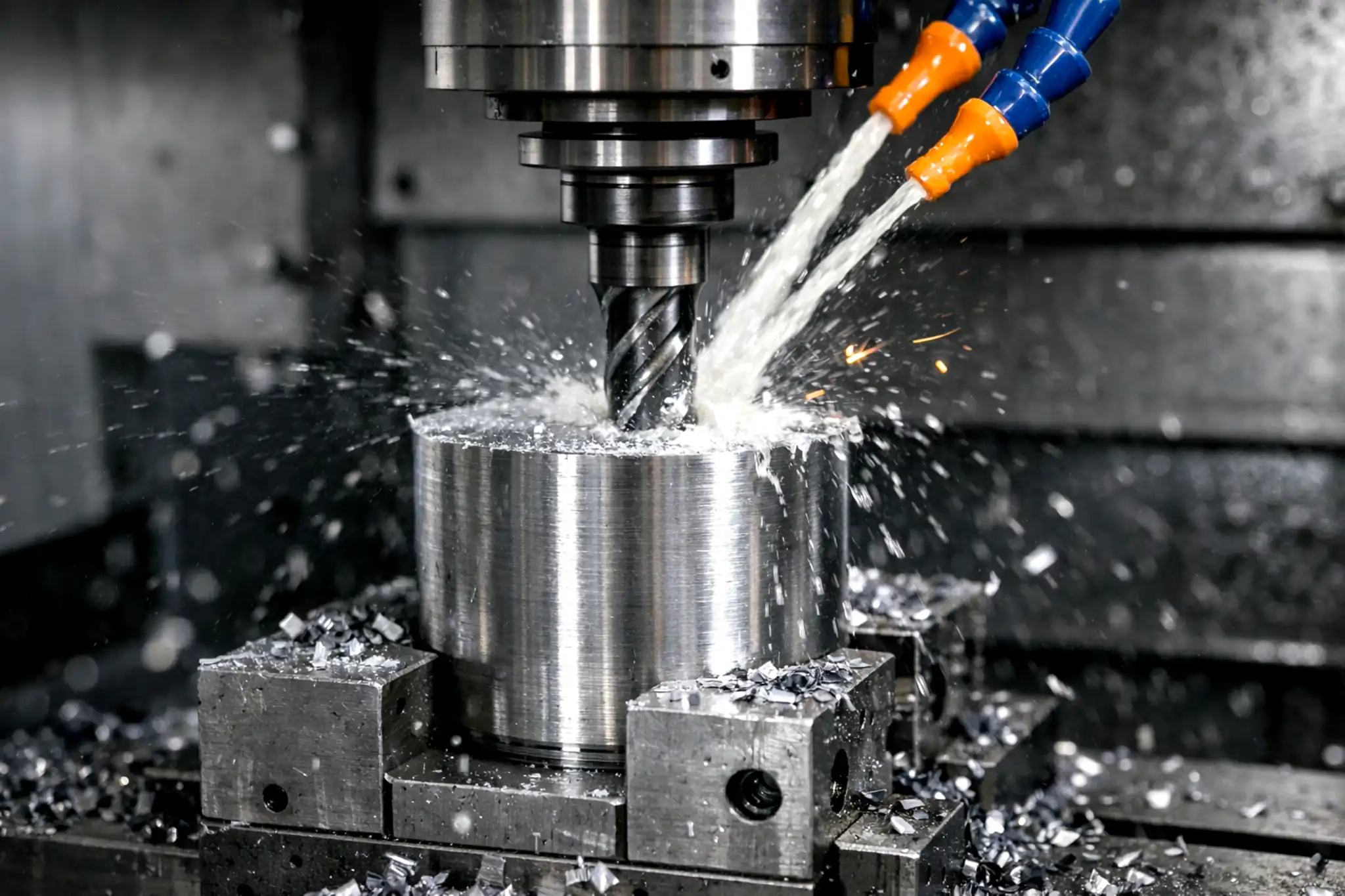
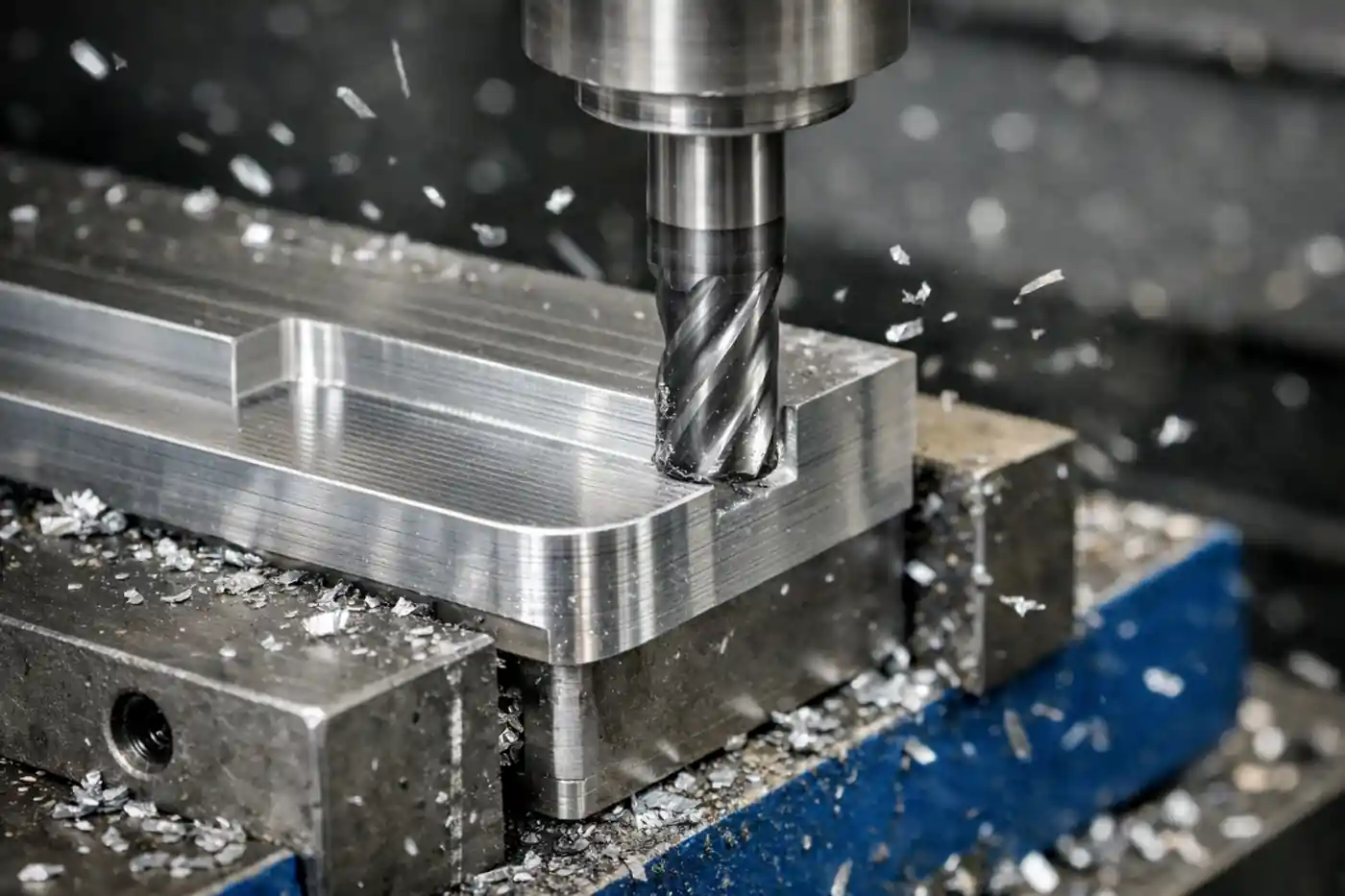
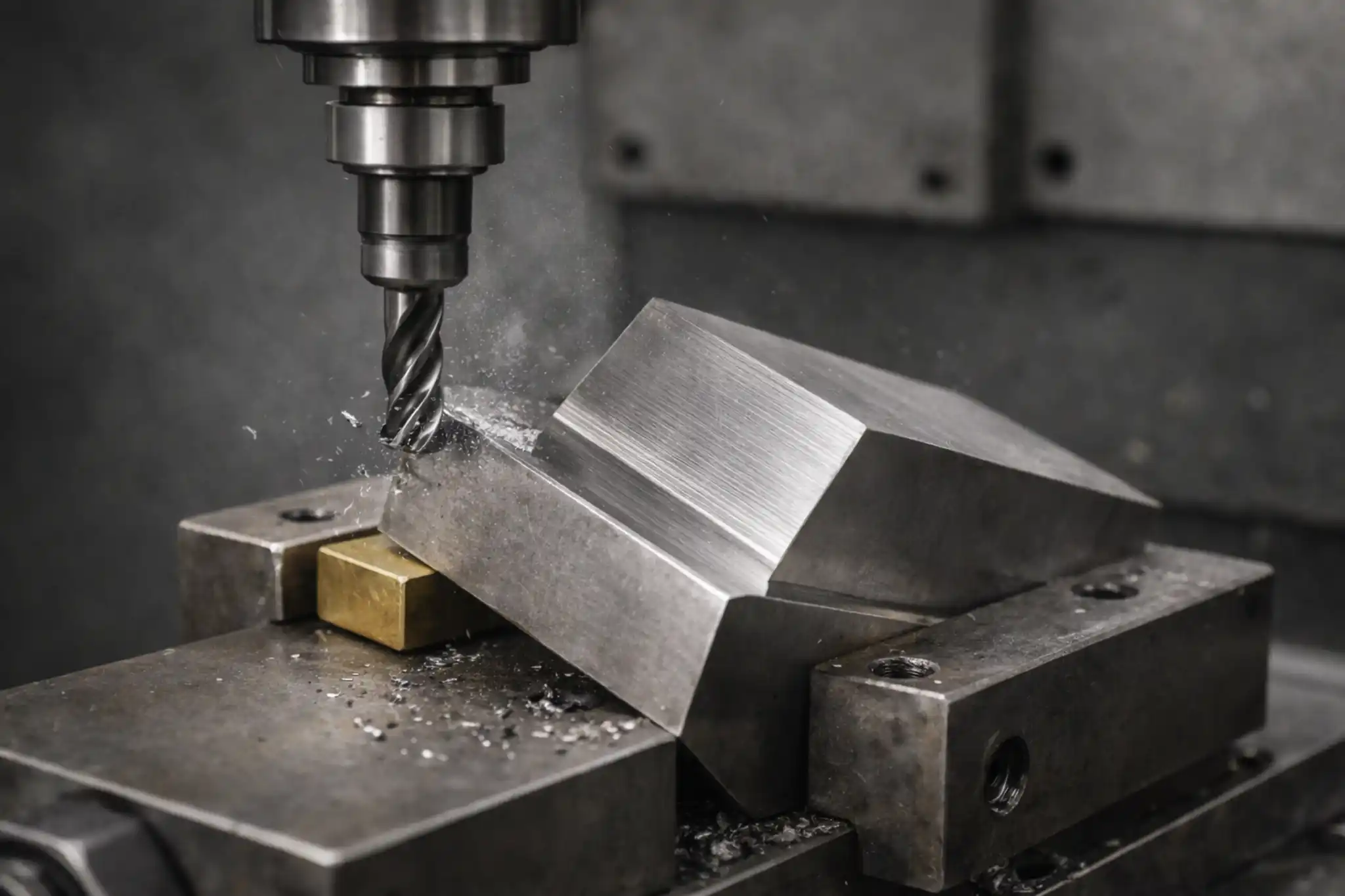
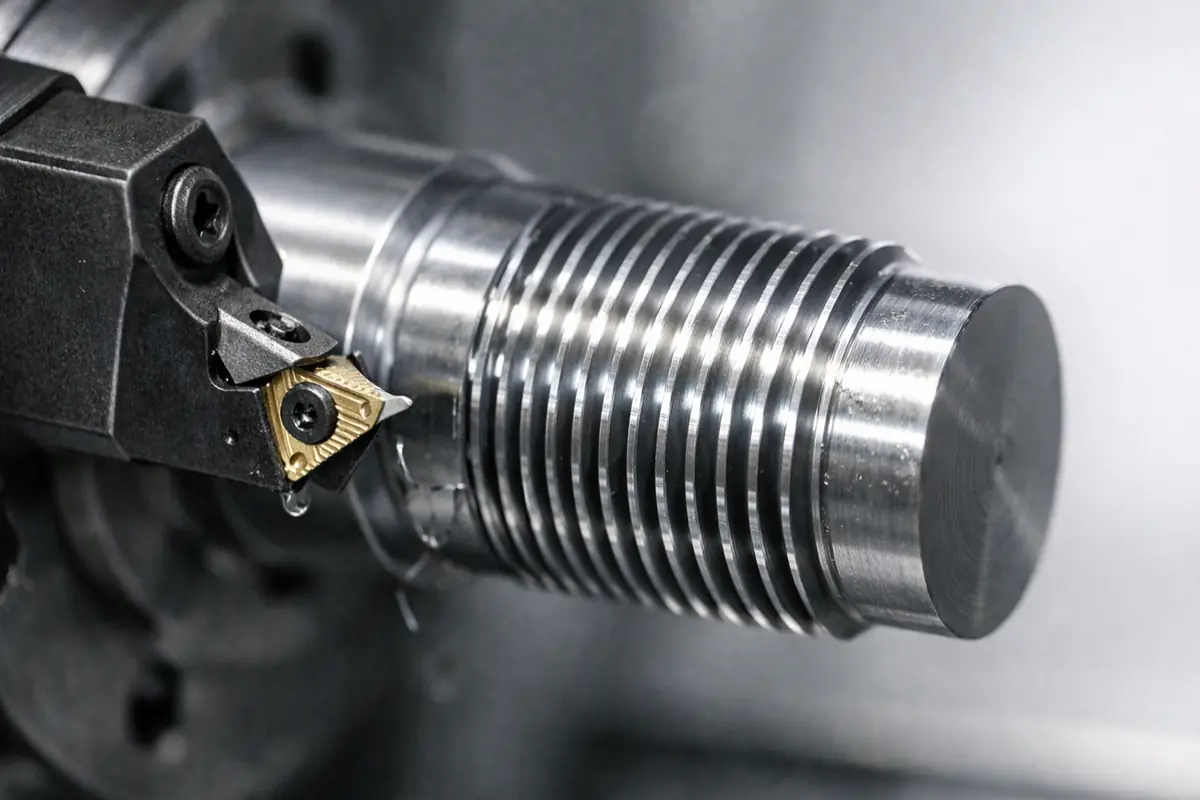
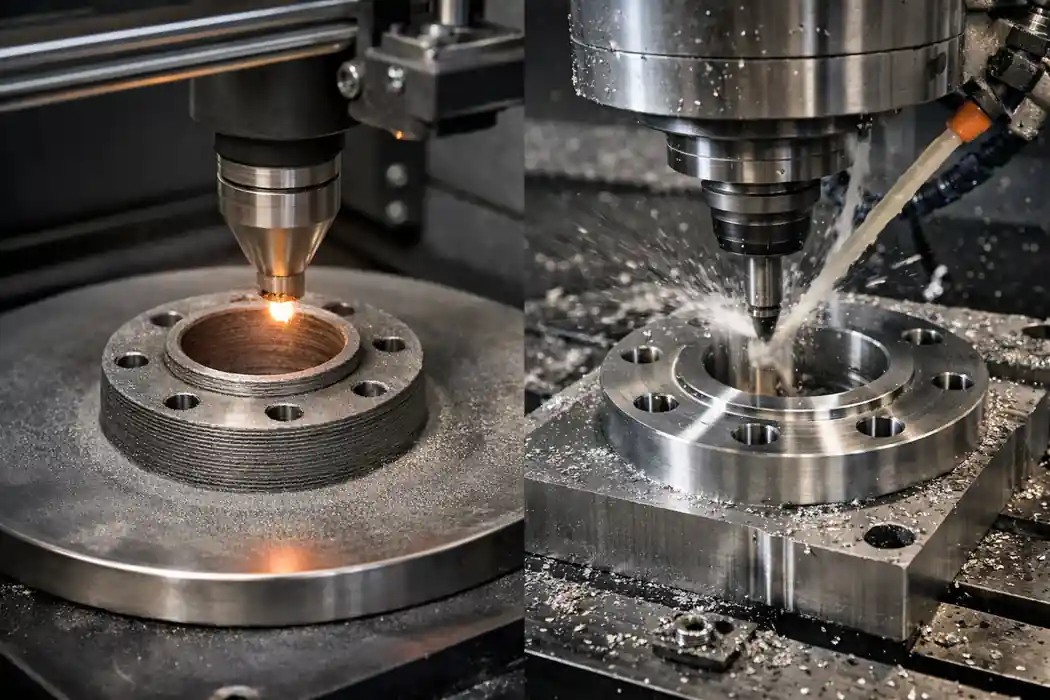
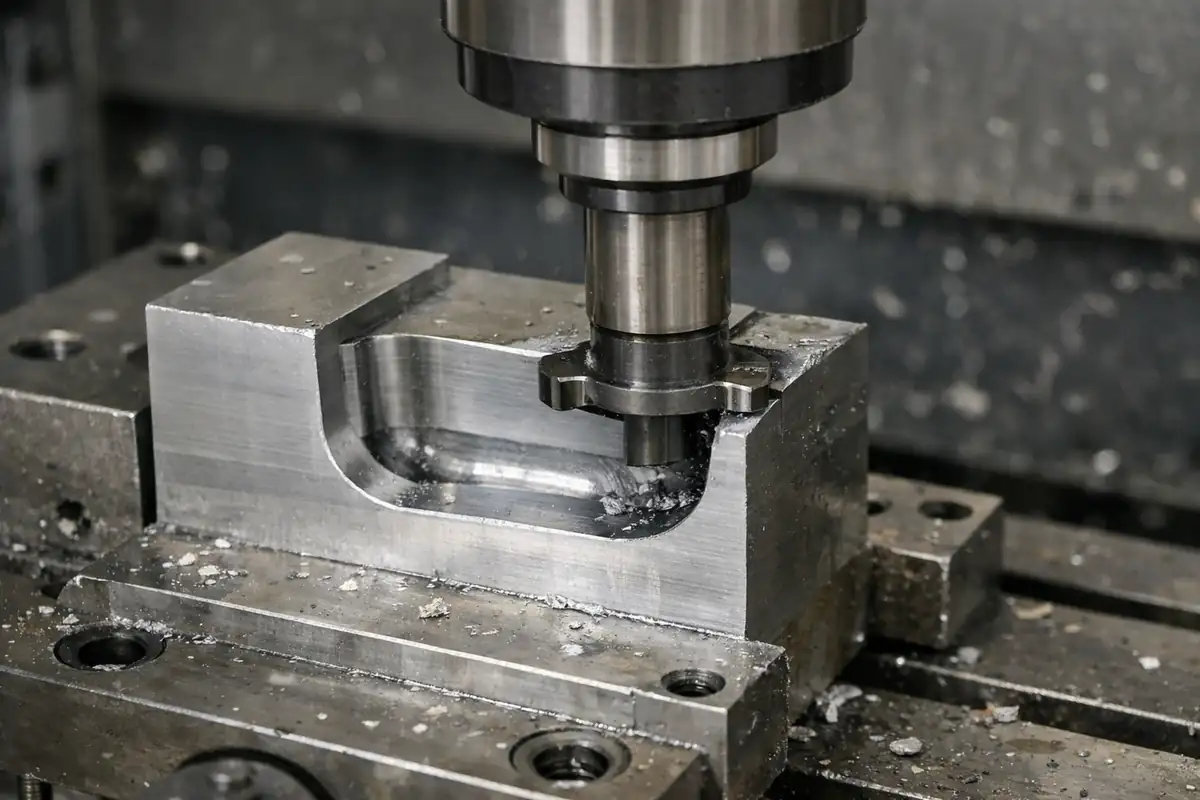
Machining Nickel and Nickel Alloys: From Material Properties to Practical Tips
Different nickel alloy families can behave very differently in machining: commercially pure nickel is more prone to adhesion and built-up edge, Monel often produces long, stringy chips, Inconel commonly shows notch wear and unstable tool life, and Hastelloy is more sensitive to heat management. This article breaks down typical problems and shop-floor symptoms by alloy family and outlines practical process controls to improve stability while meeting tolerance and surface finish requirements.
Read article