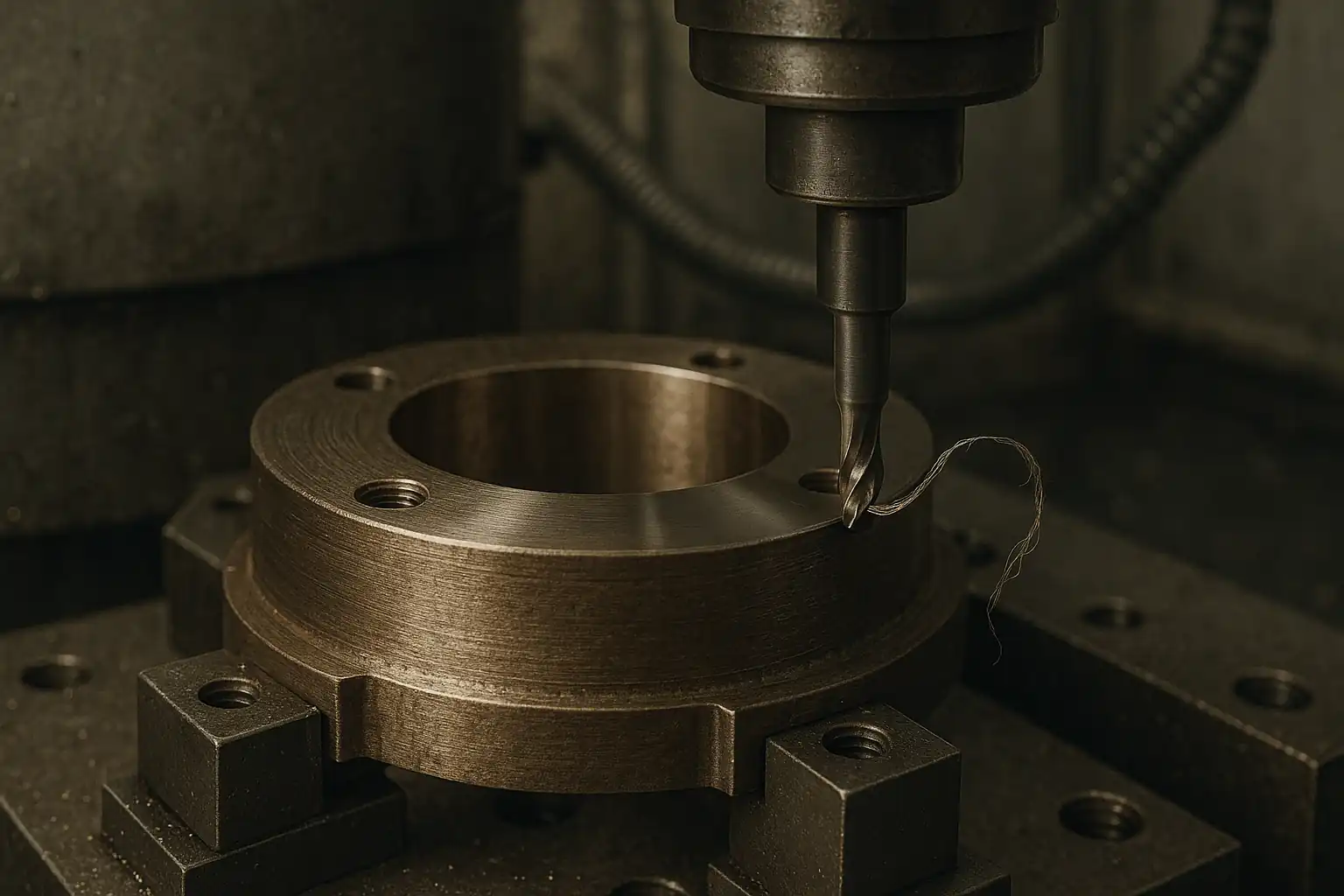
Titanium Alloys Machining: Performance, Challenges, and Best Practices
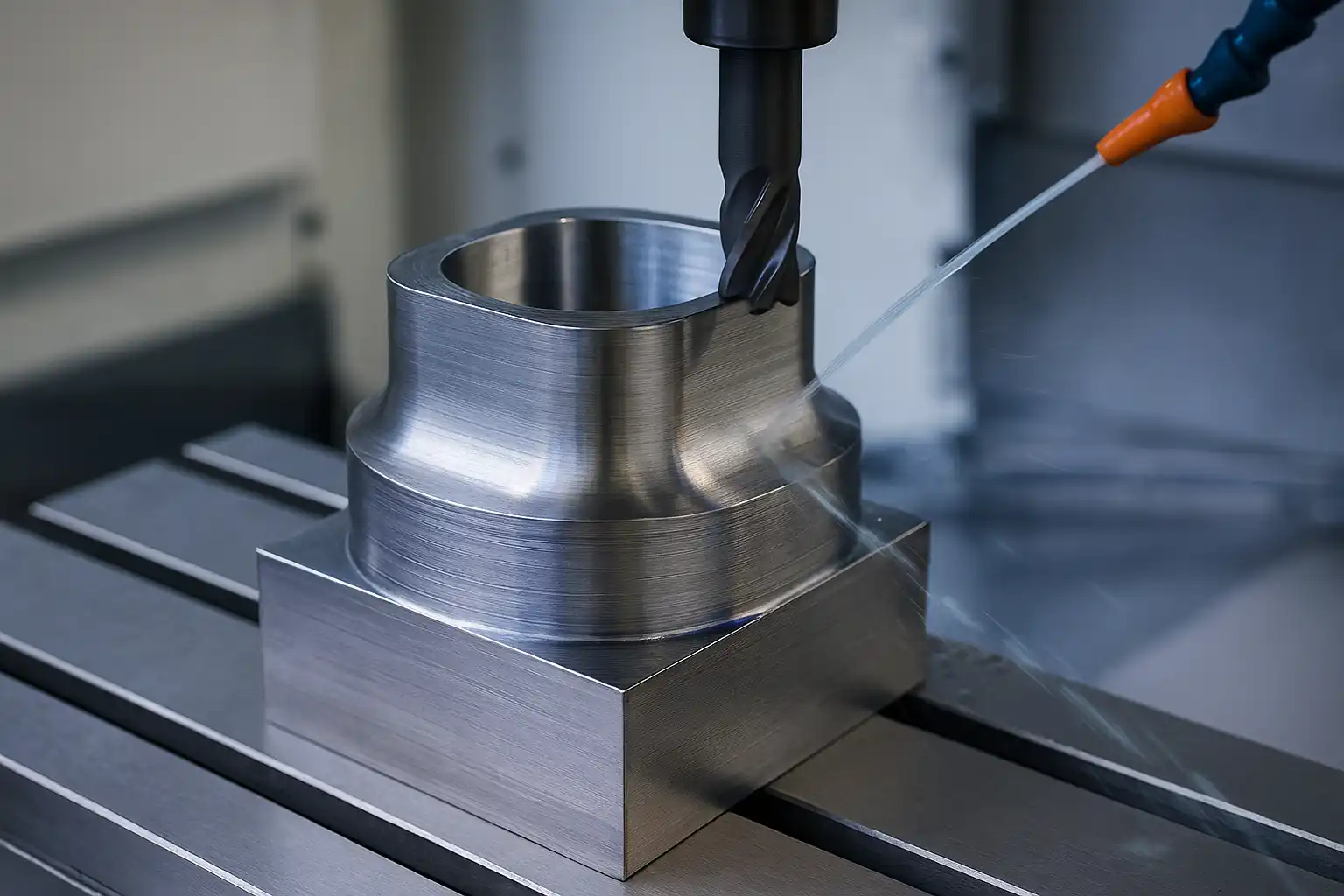
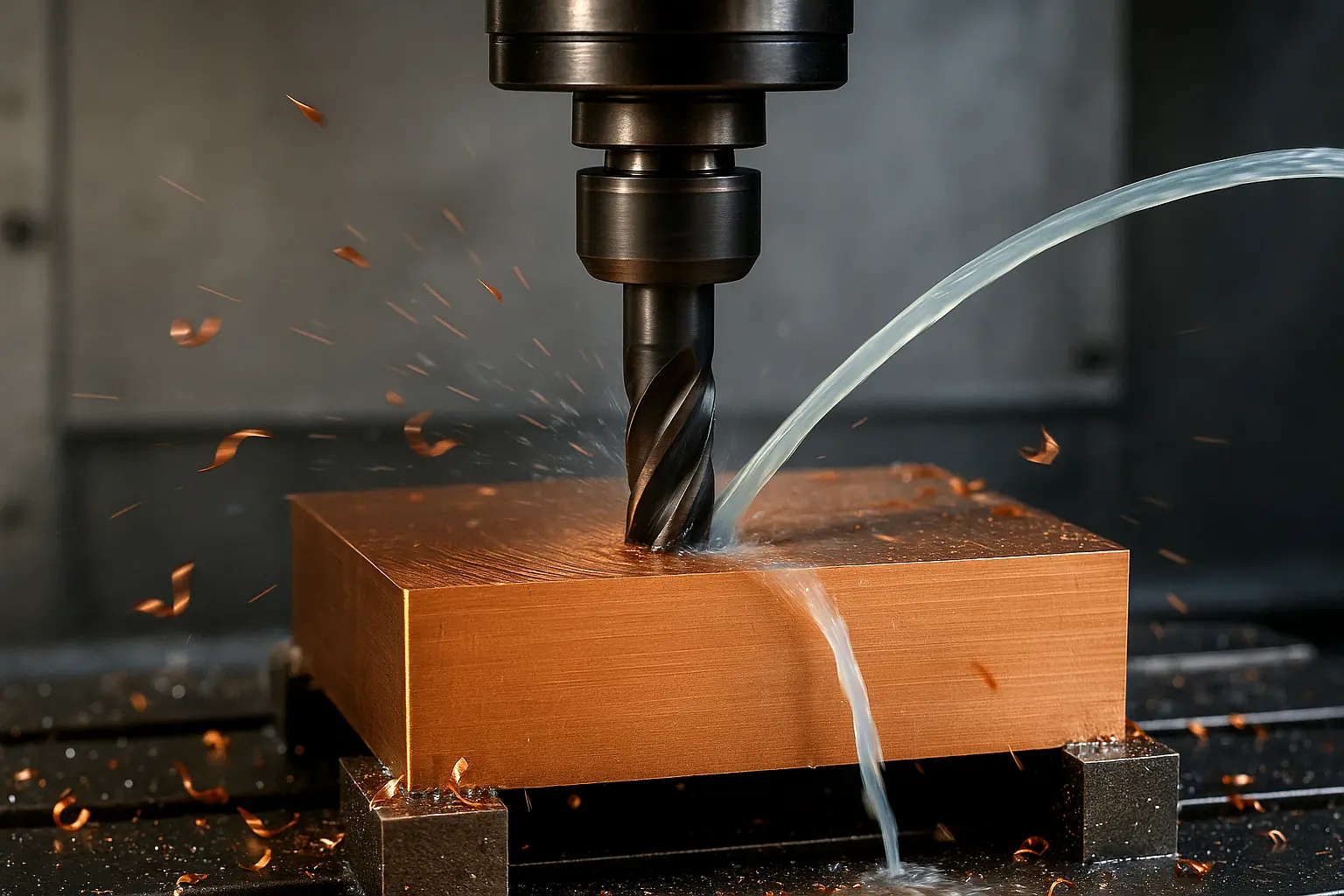
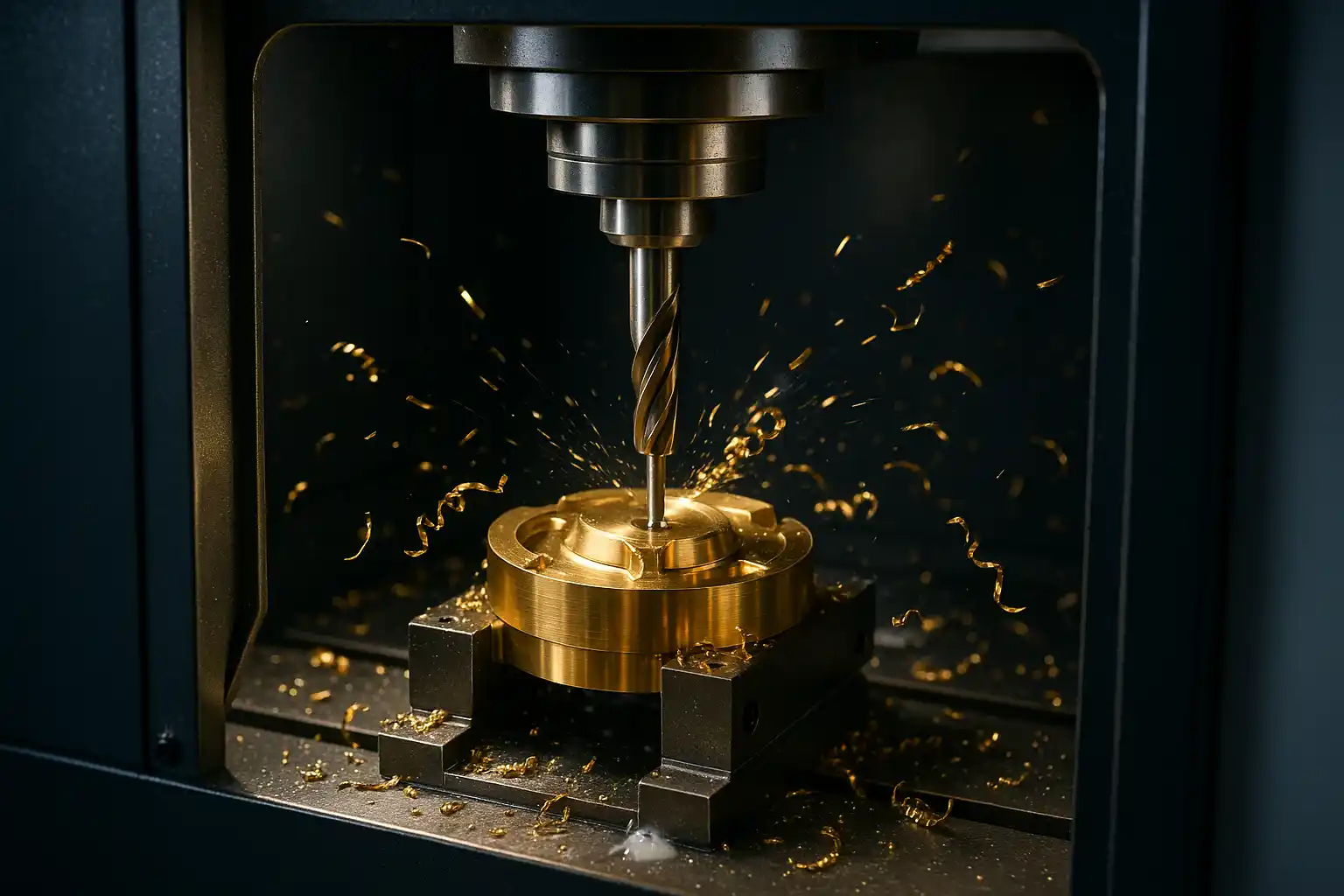
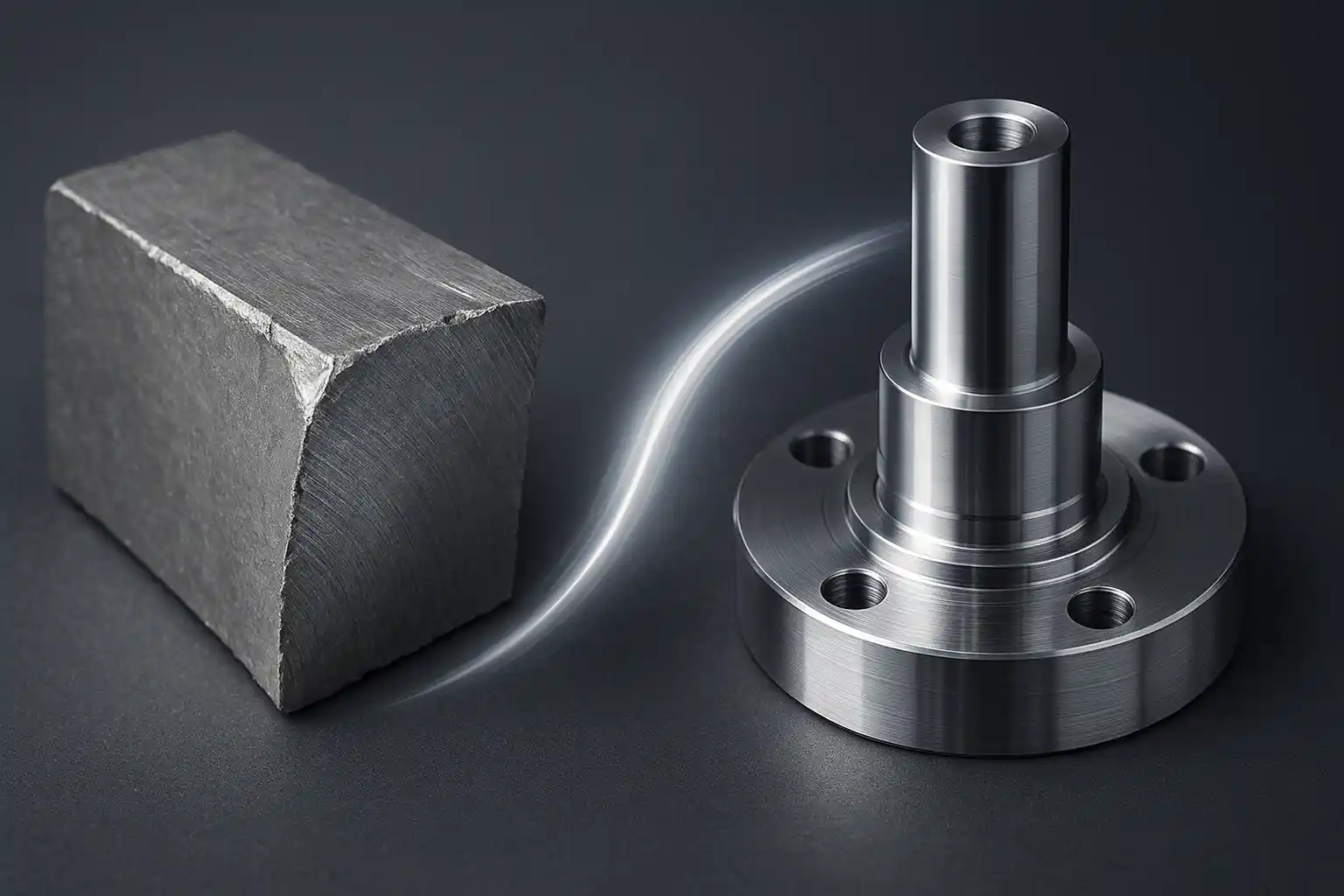
Titanium offers top strength-to-weight and corrosion resistance but machines poorly due to low thermal conductivity, chemical reactivity, and low modulus—driving heat, wear, and chatter. The stable recipe is low cutting speed (Ti-6Al-4V roughing ≈ 40–60 m/min) with higher feed to make thick chips, plus high-pressure through-coolant (70–100 bar), rigid workholding, and PVD-coated fine-grain carbide. Use low radial / high axial engagement and constant-engagement HEM toolpaths to achieve predictable tool life, tight tolerances, and clean finishes.
Read article