When it comes to manufacturing metal components, die casting and CNC machining are two of the most widely used processes. Both offer distinct advantages depending on the part’s complexity, volume, material, and budget. Understanding the differences between them is essential to choosing the right method for your project.
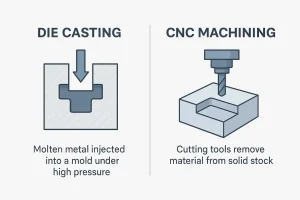
A side-by-side infographic comparing the die casting and CNC machining processes.
What Is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once cooled, the metal solidifies into the desired shape. The molds (also called dies) are typically made from hardened steel and can produce thousands of identical parts with minimal variation.
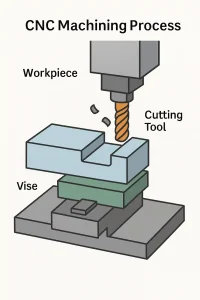
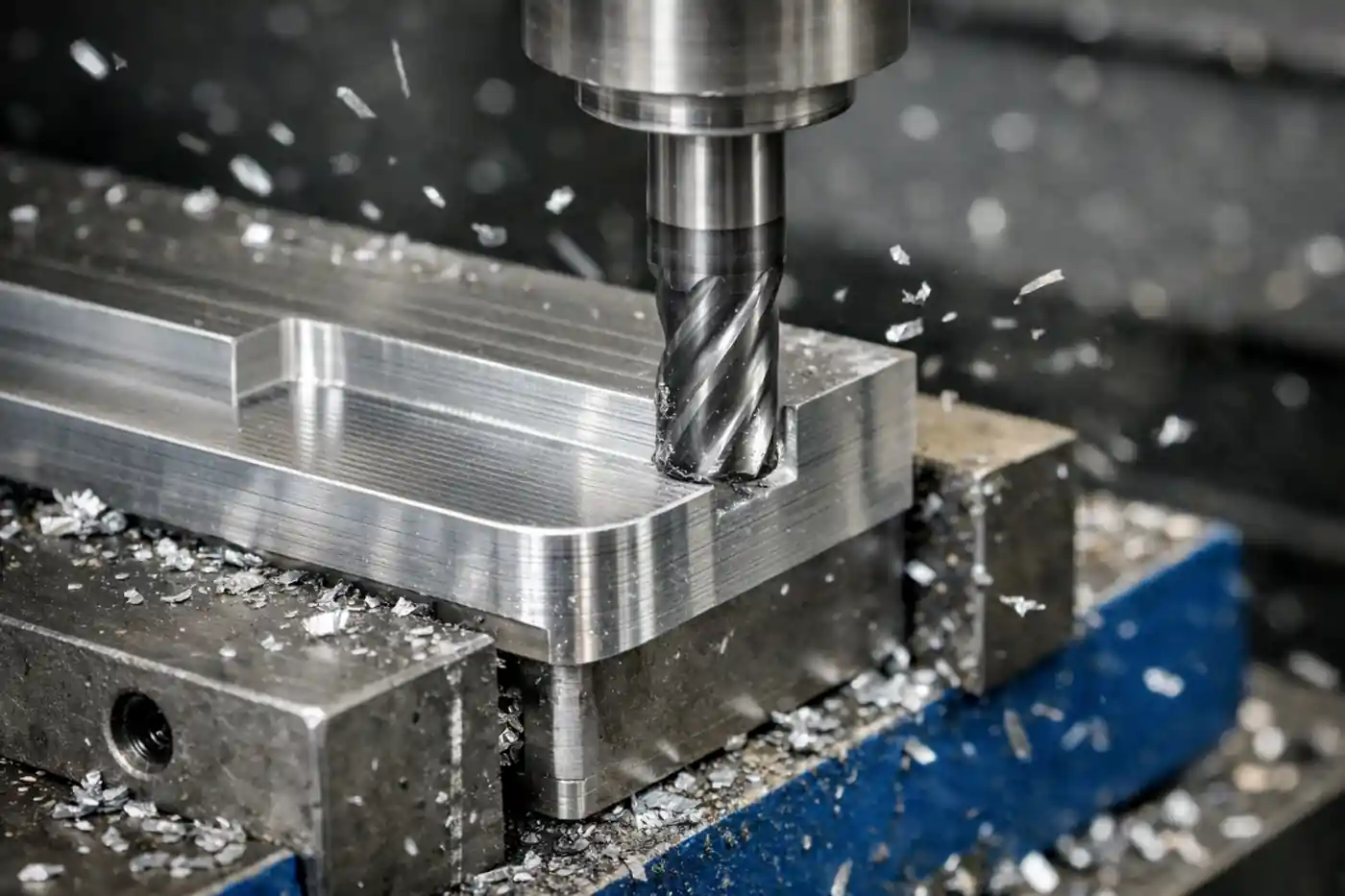
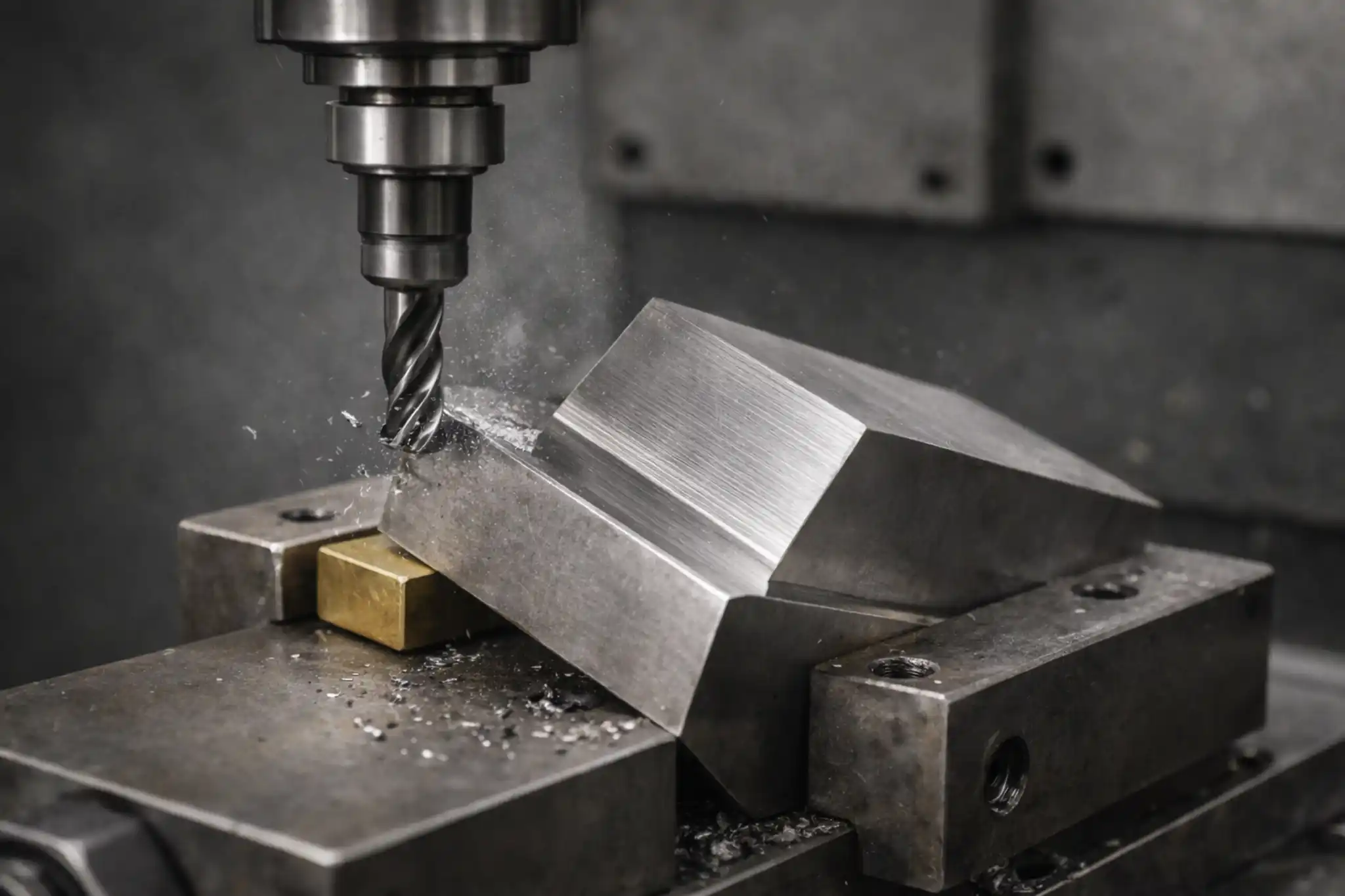
A labeled diagram showing the CNC machining process including the workpiece, vise, and cutting tool.
Key Characteristics:
- High-volume production
- Good dimensional accuracy
- Excellent surface finish
- Low material waste
Die casting is commonly used for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium components in automotive, electronics, and appliance industries.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive process that removes material from a solid block (often metal or plastic) using precision cutting tools. The process is controlled by computer programs that guide the movement of the tools.
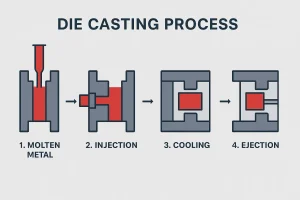
Four-stage diagram of the die casting process: molten metal, injection, cooling, and ejection.
Key Characteristics:
- High precision and tight tolerances
- Suitable for low-to-medium production volumes
- Flexible for complex geometries
- Wide material compatibility
CNC machining is ideal for prototypes, custom parts, and low-volume production where precision is critical.
Die Casting vs. CNC Machining: Key Differences
| Feature | Die Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | High (thousands of units) | Low to medium |
| Initial Cost | High (due to mold creation) | Low to moderate |
| Unit Cost | Low (after tooling investment) | Higher per unit |
| Material Waste | Minimal | Higher (subtractive process) |
| Tolerances | Moderate (can be post-machined) | Very high |
| Lead Time | Longer setup, fast production | Faster setup, slower per part |
| Best For | Mass production of metal parts | Prototypes, complex or precision parts |
Which One Should You Choose?
Choose Die Casting if:
- You need large volumes of parts (1,000+)
- The part design is relatively simple and repeatable
- You are using non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium
- You want to reduce the cost per part over time
Choose CNC Machining if:
- You need small batches or prototypes
- The part has tight tolerances or complex features
- You’re working with a wider range of materials (e.g., stainless steel, titanium)
- You require faster turnaround and greater design flexibility
Final Thoughts
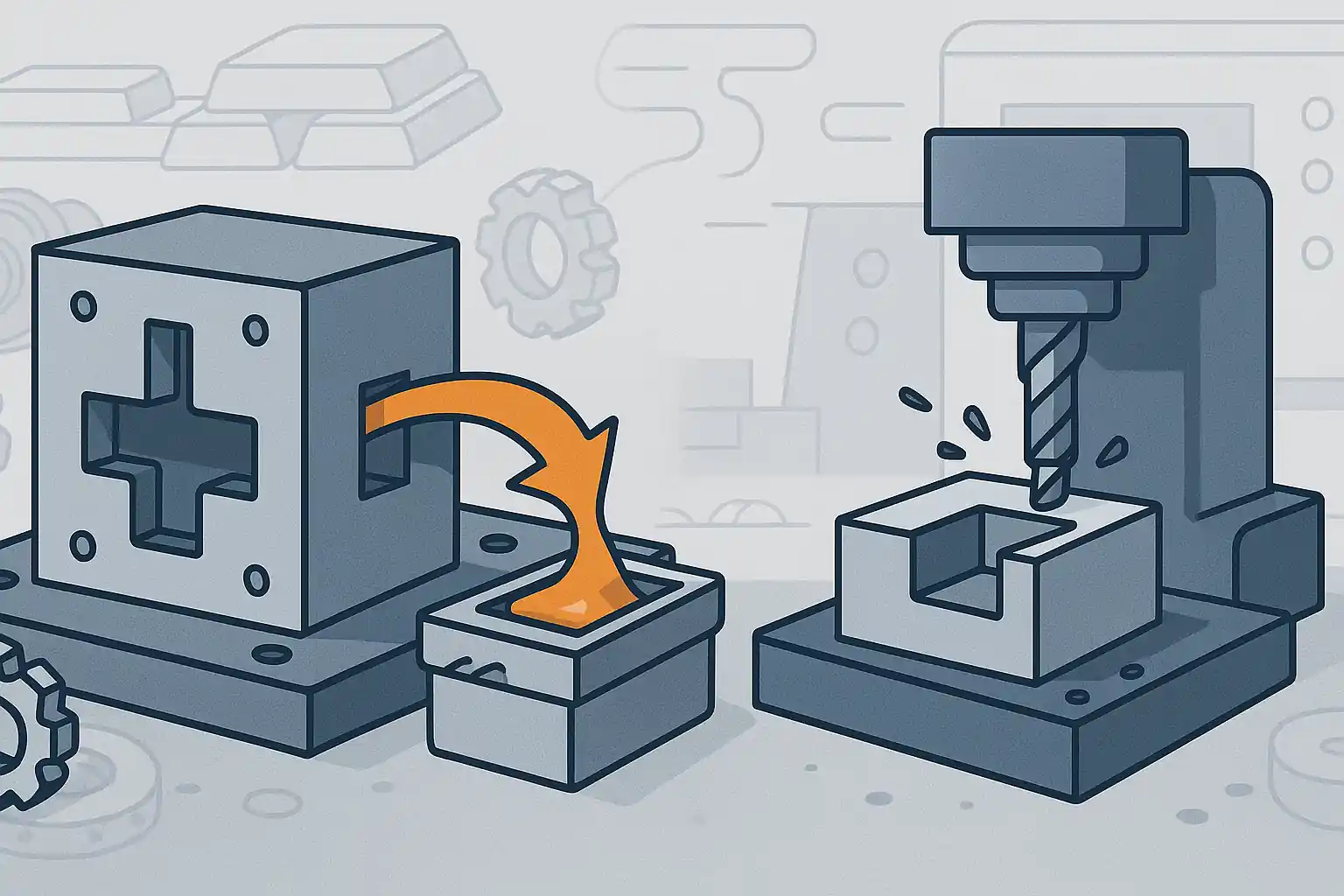
Die casting and CNC machining are not necessarily competing technologies—they are often complementary. For instance, a die-cast part may be post-processed using CNC to achieve tight tolerances on critical dimensions.
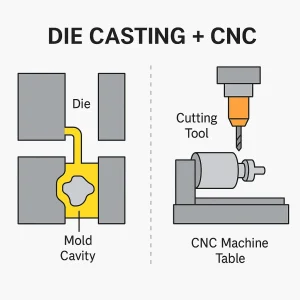
Visual representation of a hybrid manufacturing process: die casting the base shape, then finishing with CNC machining.
At Minghe, we offer both die casting and CNC machining under one roof. Whether you’re producing high-volume components or require precision-machined prototypes, our team can help you select the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing route.
Need help deciding which method suits your part? Contact us with your drawing or specifications and get expert guidance.