Introduction
In the world of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, setting the right parameters is the key to success. Have you ever faced problems like short tool life, poor surface finish, or low machining efficiency?
 The root cause often lies in a misunderstanding of the core machining parameters. Cutting speed, feed rate, and spindle speed are the “soul” of your machining process. When they work in harmony, you can achieve consistent, high-quality, and efficient results. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide for beginners, explaining the core concepts and answering common questions to help you master CNC machining parameters and transition from a novice to a proficient operator.
The root cause often lies in a misunderstanding of the core machining parameters. Cutting speed, feed rate, and spindle speed are the “soul” of your machining process. When they work in harmony, you can achieve consistent, high-quality, and efficient results. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide for beginners, explaining the core concepts and answering common questions to help you master CNC machining parameters and transition from a novice to a proficient operator.
Part 1: The Core Parameters Defined and Explained
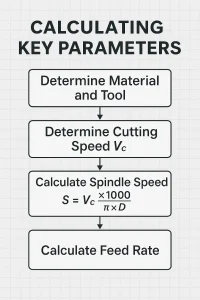
1. What is Cutting Speed (Vc)?
Cutting Speed (Vc) is the linear speed of the cutting edge relative to the workpiece’s surface, typically measured in meters per minute (m/min) or feet per minute (SFM). Simply put, imagine a car’s speed. Just as a car’s speed determines how fast you travel, cutting speed determines how fast the tool’s cutting edge “slices” through the material. Cutting speed is the most critical factor affecting tool life. Too slow, and you cause excessive friction and rubbing; too fast, and you generate too much heat, leading to rapid tool wear or even tool failure.
2. What is Spindle Speed (S)?
Spindle Speed (S) is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM) of the machine’s spindle. This is the parameter you will most frequently input into your CNC machine. It’s not an independent parameter, but is calculated from the cutting speed, as different tool diameters require different RPMs to achieve the same linear cutting speed.
Calculation Formula:
S=(Vc×1000)/(π×D)
- S: Spindle Speed (RPM)
- Vc: Cutting Speed (m/min)
- π: Pi (approximately 3.14)
- D: Tool Diameter (mm)
3. What is Feed Rate (f)?
Feed Rate (f) is the speed at which the cutting tool moves into the workpiece, typically measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min) or inches per minute (IPM). Feed rate determines your machining efficiency and the final surface finish. Think of it as the speed at which you push a knife through a piece of bread. Too fast, and you get a rough cut; too slow, and you’re inefficient, causing excessive heat from rubbing.
Calculation Formula:
f=ft×Z×S
- f: Feed Rate (mm/min)
- ft: Feed per tooth (mm/tooth)
- Z: The number of cutting teeth or flutes on the tool.
- S: Spindle Speed (RPM)
4. The Interconnected Relationship: A Logical Chain of Command
These three parameters are not isolated; they are fundamentally linked and must be set in a logical sequence. You can follow this simple chain: Cutting Speed (depends on material and tool) → Spindle Speed (calculated from Vc and D) → Feed Rate (calculated from ft, Z, and S). First, you determine the optimal cutting speed based on the workpiece material and tool type. Second, you use that cutting speed to calculate the spindle speed you need to set on your machine. Finally, you calculate the feed rate based on the number of teeth on your tool and the desired chip load. By following this logical flow, you arrive at a complete set of CNC machine cutting parameters.
Part 2: Common Questions & Practical Applications
5. Why is My Tool Breaking or Wearing Out So Quickly?
This is often a direct symptom of improperly set CNC machining parameters. The most common cause is excessive cutting speed, which causes the tool to overheat and wear out rapidly. Another reason is a feed rate that is too low, causing the tool to rub against the material excessively, leading to accelerated wear. The solution is to either lower the cutting speed or increase the feed rate, ensuring you have proper coolant flow.
6. How Can I Get Rid of Chatter (Vibration) During Machining?
Chatter is a common problem in CNC machining. It’s usually caused by excessive tool overhang, mismatched cutting parameters, or a lack of rigidity in the machine setup. To fix it, try adjusting the spindle speed (usually by slightly increasing or decreasing it), reducing the depth of cut or feed rate, or using a shorter, more rigid tool.
7. How Do Parameters Differ Between Materials Like Aluminum and Stainless Steel?
The physical properties of different materials dictate their optimal cutting parameters. For example, aluminum CNC machining parameters typically require high cutting speeds and feed rates to quickly evacuate chips and prevent melting. In contrast, stainless steel CNC machining parameters require lower cutting speeds to reduce heat and the use of coated tools to improve wear resistance.
8. What’s the Difference Between Lathe and Mill Parameter Settings?
While the core parameters are similar, the biggest difference between a lathe and a mill is the unit for the feed rate. A mill’s feed rate is in millimeters per minute (mm/min), while a lathe’s feed rate is typically in millimeters per revolution (mm/rev), which specifies the distance the tool travels for every single rotation of the workpiece.
Part 3: Best Practices & Pro Tips
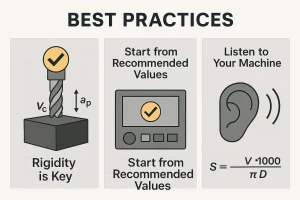
9. Master These Best Practices to Work Smarter, Not Harder
- Rigidity is Key: Always ensure your workpiece and cutting tool are securely clamped. A rigid setup is a prerequisite for achieving optimal cutting parameters and preventing chatter.
- Start with Recommended Values: Don’t guess your parameters. Always use a reference chart or a reliable calculator as a starting point.
- Listen to Your Machine: The sound of a cut is the best indicator of its quality. A smooth, consistent cutting sound is a good sign, while a high-pitched squeal or a loud banging noise indicates a problem that needs immediate parameter adjustment.
10. Where Can I Find a Complete CNC Machining Parameters Chart?
Many professional tool manufacturers and machine companies offer high-quality, free resources. If you need a complete parameters chart or an online calculator, we recommend visiting the following websites:
Using these professional tools, you can easily find the optimal parameters for your machining tasks.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering the relationship between cutting speed, spindle speed, and feed rate is the most crucial step in CNC machining. By scientifically calculating and setting these parameters, you can effectively prevent common problems like tool breakage and poor surface finish, while also significantly improving your production efficiency. Ready to apply this knowledge? Check out our CNC Machining Parameters Calculator and get your first optimized settings in minutes!



