In the landscape of modern manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining holds a central position due to its unparalleled precision and automation capabilities. It has made the production of complex parts both efficient and controllable. However, within this broad technology, CNC turning and CNC milling are two distinct and equally vital machining methods. They are often confused, but each has a unique working principle and application scope. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of the essence of these two processes, revealing their key differences to help you make more informed decisions when choosing a machining solution.
What is CNC Turning?
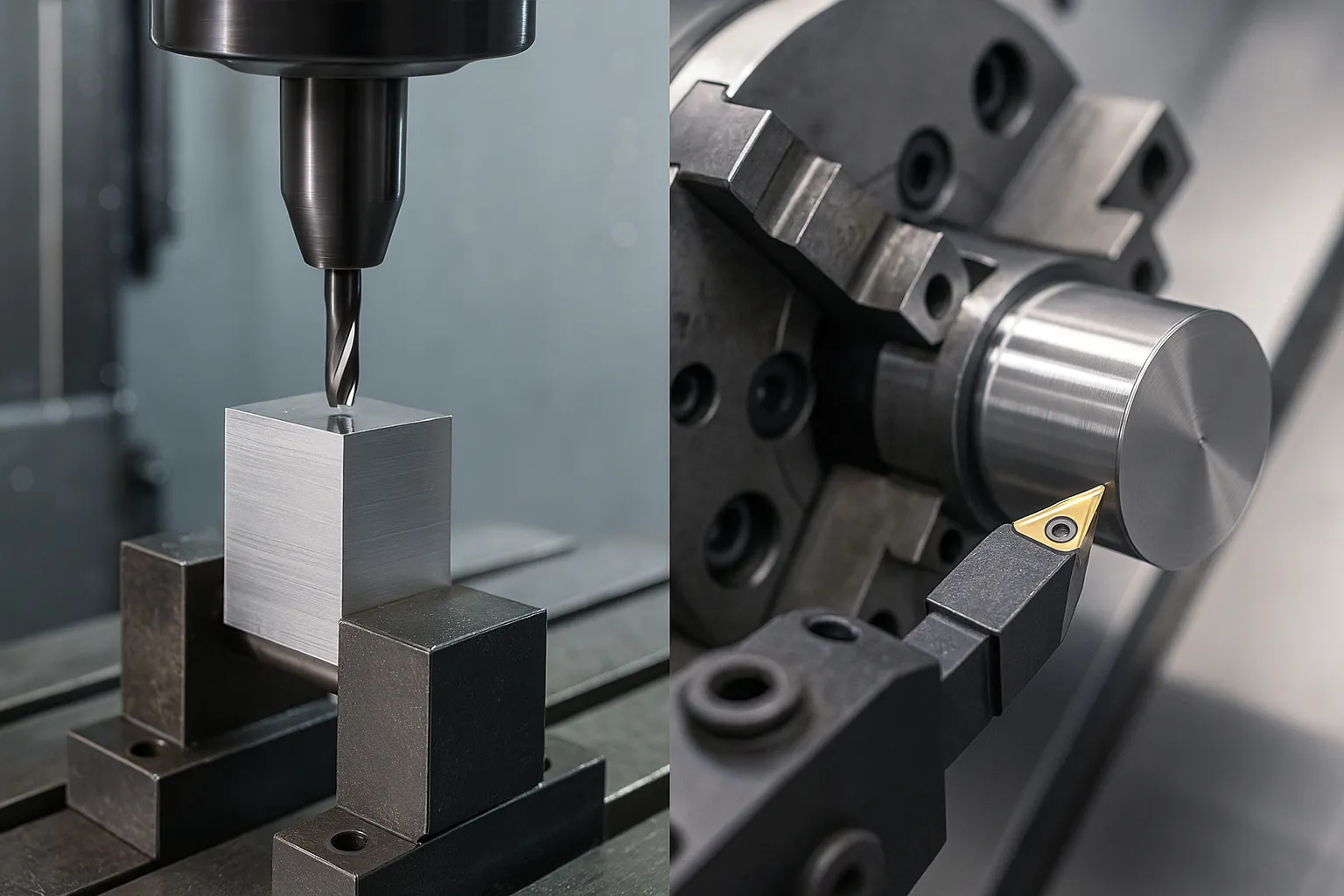
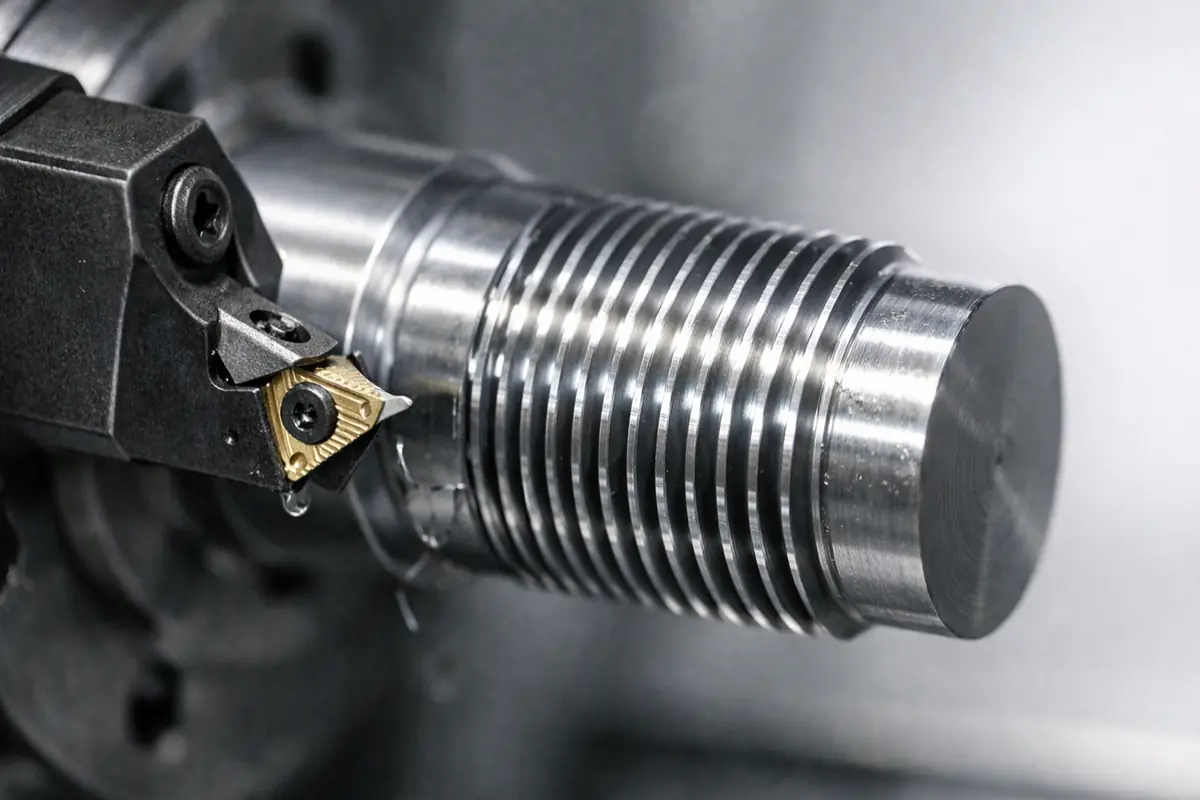
CNC turning is a subtractive manufacturing process based on rotational symmetry. Its core principle is to have the workpiece (raw material) rotate at high speeds on the main spindle, while the cutting tool remains stationary. The tool moves linearly along the exterior or interior contours of the workpiece. By precisely controlling the feed rate and depth of the tool, the machine can remove material layer by layer, ultimately forming high-precision symmetrical parts such as circles, cylinders, cones, or threads.
This process is primarily performed on a CNC lathe or turning center. It is capable of producing not only simple parts like shafts and pins but also more complex rotational bodies by combining various operations like knurling, boring, and drilling. With its high efficiency and precision, CNC turning is widely used in automotive, aerospace, medical equipment, and many other industries.
What is CNC Milling?
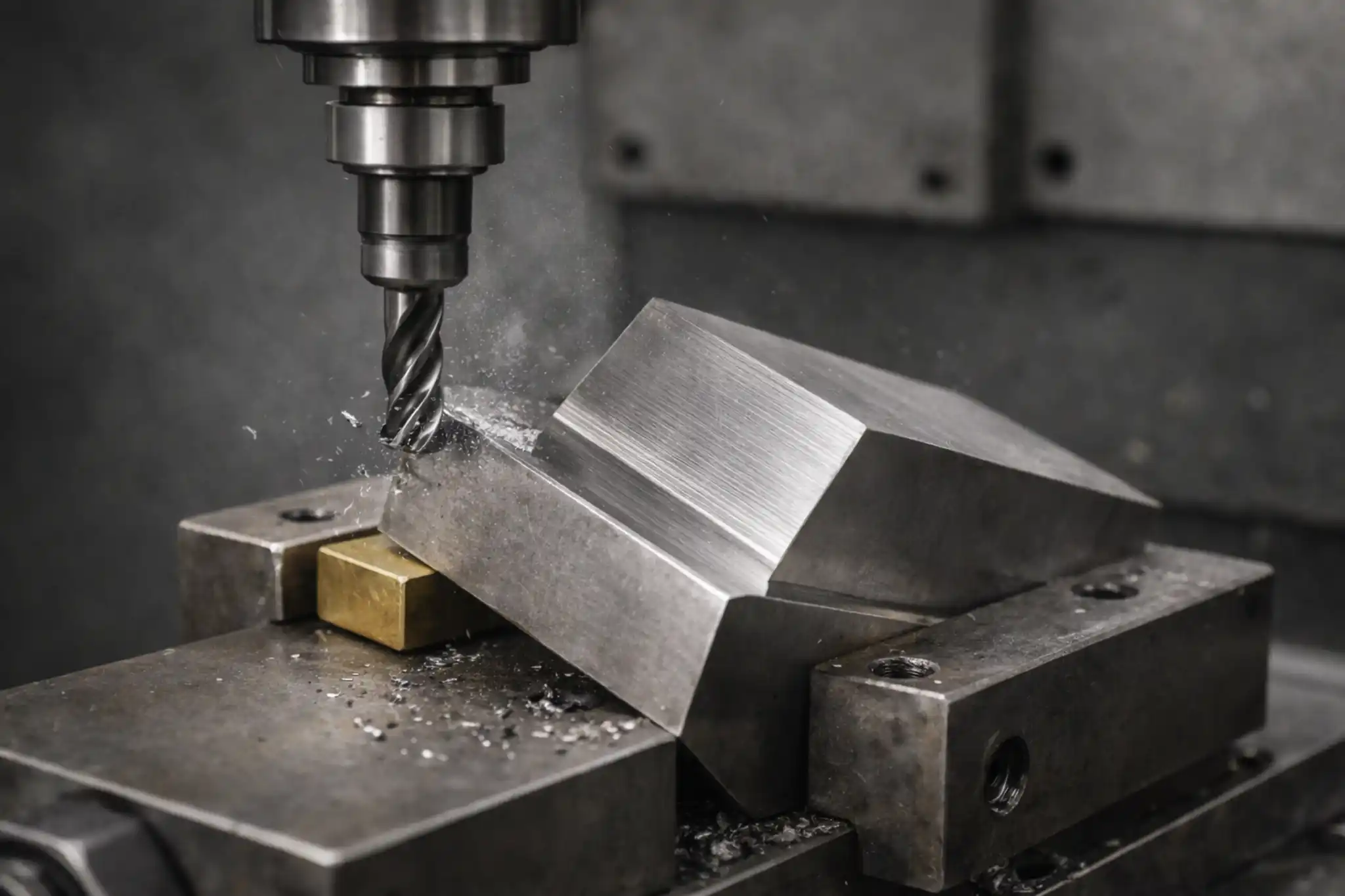
In contrast to turning, CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process based on tool rotation. Its working principle is to have a multi-point cutting tool (milling cutter) rotate at high speeds to remove material from the workpiece. Simultaneously, the workpiece is securely clamped on a table and moved in three-dimensional space (X, Y, and Z axes) according to the program to achieve a complex cutting path.
CNC milling is mainly carried out on a CNC milling machine or machining center. It is not limited by rotational symmetry and can easily produce a wide range of complex three-dimensional geometric shapes, including flat surfaces, grooves, keyways, curves, and various irregular holes. Consequently, milling plays a crucial role in mold making, structural part processing, and the production of complex casings.
What is the Difference Between CNC Milling and Turning?
While both are subtractive manufacturing techniques, they have fundamental differences in the following key aspects:
| Comparison Dimension | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
| Working Principle | Workpiece rotates, tool is stationary | Tool rotates, workpiece is stationary |
| Primary Function | Manufacturing parts with rotational symmetry | Manufacturing complex 3D geometric parts |
| Processing Advantages | High cost-effectiveness, fast processing speed | High flexibility, capable of complex shapes |
| Application Limitations | Limited to rotationally symmetrical parts | High cutting force, faster tool wear |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Machining Solution
Ultimately, the choice between CNC turning and CNC milling depends on the shape and function of your required parts. For rotationally symmetrical components like shafts and pins, turning is the ideal choice due to its high efficiency and cost advantages. Conversely, for asymmetrical parts that require grooves, holes, or complex surfaces, milling is the indispensable technology.
Minhe is a company with deep expertise in multi-axis milling and turning, providing comprehensive CNC machining services tailored to our clients’ applications. With our technical proficiency, we can precisely, efficiently, and economically produce high-quality finished components from your design drawings.Contact us today for a free consultation and quote on your next project.